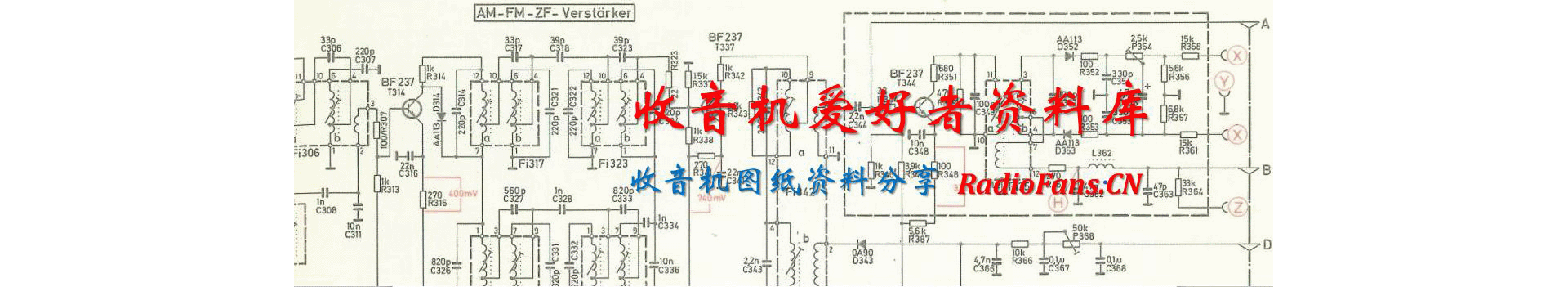
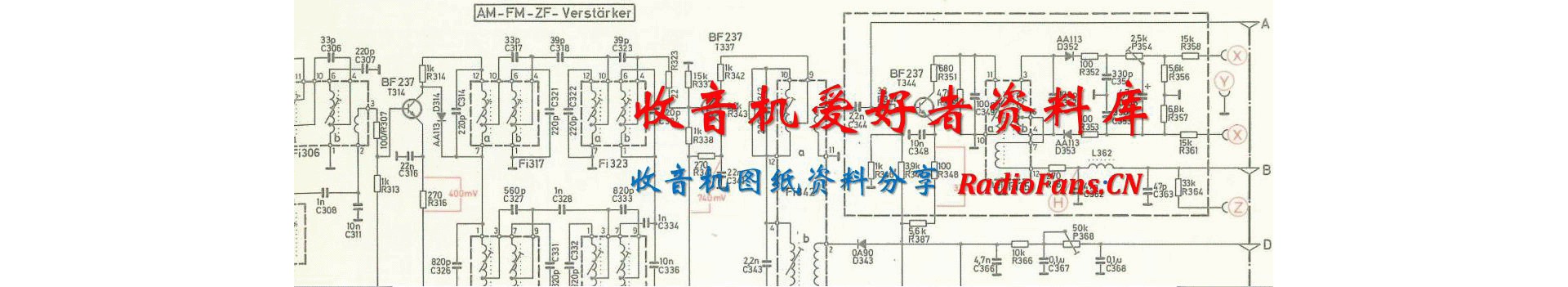
 Arcam-DV88-dvd-sm维修电路原理图.pdf
Arcam-DV88-dvd-sm维修电路原理图.pdf
《Arcam-DV88-dvd-sm维修电路原理图.pdf》由会员分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《Arcam-DV88-dvd-sm维修电路原理图.pdf(60页珍藏版)》请在收音机爱好者资料库上搜索。
1、DV88 DiVA DV88 DVD Player + Progressive Scan Service Manual ARCAM Issue 2.0 RadioFans.CN 收音机爱 好者资料库 Contents List ! Contents list ! Circuit description ! Frequently asked questions issue 1 ! Software release notes 1.1 to 1.76 ! Progressive scan upgrade instructions ! Service guide ! Circuit diagrams
2、 ! Component overlays ! Circuit board parts list ! General assembly parts list RadioFans.CN 收音机爱 好者资料库 Circuit Descriptions L875 DSP Circuit Summary This board is used in the DV88 and DV27 DVD players. It can be considered to be the central digital core of the player, and is based around the Zoran V
3、addis III DVD decoder IC. A Siemens C161 microcontroller is used as the system CPU and software runs on this which controls the whole system. A video DAC is also present, as well as an ATAPI bridge device. The board interfaces with the display board, the DVD drive, and the AV board. Overview The hea
4、rt of the system is the Zoran Vaddis III IC, which receives a data stream on its AV interface. The chip has 2 separate DSPs, one for audio and one for video. The MPEG video/ audio decoding and Dolby digital audio decoding are performed in these DSPs as well as other post processing on audio and vide
5、o, OSD generation, decryption of DVD and other functions. The vaddis is controlled by the system CPU via its host bus interface. The system uses an ATAPI type DVD drive. With the AV interface the Vaddis AV input comes directly from the drive, and the drive is controlled from the system CPU via an SS
6、C bus (standard synchronous control). The design was modified to use the ATAPI standard by the inclusion of the ATAPI bridge chip. This has an ATAPI interface to the drive, and an SSC interface to the CPU. A data stream is provided which interfaces to the Vaddis AV input. On the output side of the s
7、ystem, the digital audio output from the Vaddis is passed to the AV board in I2S format. The video output from the Vaddis is in the form of a digital 8 bit parallel bus, with 27MHz clock, containing multiplexed chroma and luma data. H and V synchronisation is performed by the use of embedded sync pa
8、tterns in the data. This type of bus is a standard interface known as BT-656. This bus connects to the video DAC, an Analog Devices ADV7172. This does PAL/NTSC encoding and D-A conversion, and gives out 6 channels of analogue video. These are composite, S-Video, and 3 lines that are switchable YUV/R
9、GB. All video outputs are passed to the AV board where they are filtered and buffered before going to the outside world. Circuit Description Refer to L875 circuit diagrams Sheet 1 - Top level This is the top level of the schematic and shows how the sheets link together plus some of the board interfa
10、ces. CN8 provides a serial port which may be connected to a PC via an RS232 transceiver, for debugging purposes. CN6 is the interface to the front panel. A 4 wire serial interface communicates with the VFD driver chip, which drives the display, scans the buttons and drives the LEDs on the front pane
11、l. This interface consists of FPDIN (serial data from panel), FPSEL (chip select), FPCLK (serial clock) and FPDOUT (serial data to front panel). IRIRQ is the signal from the IR remote receiver on the front panel, driven by an open collector circuit. This is because that line also goes to the progres
12、sive scan board in the DV27, which has the remote bus input on it. CN1 is the power input. +5V and +3.3V rails are provided. The Vaddis and its SDRAM operate on 3.3V, everything else runs on +5V. CN5 is the audio connector to the AV board. Digital audio in I2S and SPDIF formats are passed to the AV
13、board from here, as well as a number of control signals: FSEL0.1 Selects 1 of 4 audio clock frequencies MD, MC, ML8716_L, ML_8716_R, ML_8716_X 5 wire SPI bus to configure audio DACs GAIN_SCALING HDCD gain scaling signal. The audio master clock also comes on to the board here. It is generated on the
14、AV board and fed to the DSP board to synchronise the audio, of which more later. CN2 and CN3 are not fitted. They are the AV and host interface for the AV type drive that the system was originally designed to use. Sheet 2 - CPU The system CPU, U3, is a Siemens C161 16 bit ROM-less microcontroller ru
15、nning at 16MHz. ROM and RAM are external to the micro, so we have a CPU bus with 19 bits of address and 16 bits of data. The ROM memory is provided by U4 and U5 which contain the lower and upper 8 bits of program memory respectively. These are 28SF040 4Mbit (512K x 8) FLASH EEPROMs. These must be pr
16、ogrammed and fitted in their sockets before the board can be tested. Once in place they can be re-programmed in system, and the software has a feature where new software can be uploaded from a CD. It is important to note that these devices are re-programmable. The system RAM is provided by U6 and 7
17、which contain the lower and upper 8 bits of memory respectively. These are 1 Mbit (128K x 8) devices, making 256KByte memory altogether. U12 is an 8 bit wide latch that provides a few extra control output lines - these being a 5 wire serial control interface for the audio DACs, a reset signal for th
18、e AV drive (not used), and 16/9 which is used on the SCART status line. U1 is a power on reset generator, this resets the micro, and the micro has an output RSTOUT which provides the signal RESET. This goes to many devices on this board and the AV board and progressive scan board. U2 is a serial EEP
19、ROM, providing non-volatile storage of setup data. All the parameters from the setup menu are stored here, as well as bookmarks and the region code. The resistor packs RP1-3, are important pullup/pulldown resistors which configure the mode of the micro on power up. The resistors R2 and R12-15 are pr
20、ovided so we may configure the board for different devices. All must be fitted except R12 and R15 for normal configuration. Sheet 3 - Vaddis DVD decoder This sheet shows the Vaddis DVD decoder IC, U8, and its associated components. Going back to the block diagram, various bus interfaces were mention
21、ed. These can be seen on the schematic as follows: The AV interface This is used for carrying audio/video data from the ATAPI bridge to the Vaddis. The following lines are used. DVDDAT0:7 8 bit parallel data DVDSTRB Strobe signal DVDSOS Start of sector indicator DVDVALID Valid data indicator DVDREQ
22、Request signal (Vaddis output) DVDERR is not actually used in the ATAPI configuration we are using. The HOST bus interface The CPU uses this to control the Vaddis, it carries information both to and from the micro. HD0.7 The lower 8 bits of the system data bus HA1.4 Lower 4 bits of system address bu
23、s HWR- Write strobe HRD- Read strobe MPGCS- Chip select MPEGIRQ-Interrupt line generated by Vaddis Digital Video bus The 8 bit bus YUV0:7, with CLK27 provides the BT-656 type parallel digital video bus. The 27MHz clock is provided on 2 different lines. CLK27 is used for the video DAC (and also goes
24、to the ATAPI chip). CLK27PS is used for the progressive scan board. Digital Audio The audio output of the Vaddis is given out on the following signals SPDIF-I34 IEC 958 SPDIF output ASDAT0 Serial data for Left and right ASDAT1 Serial data for Lsurround, ASDAT2 Serial data for Centre, sub ALRCLK Word
- 配套讲稿:
如PPT文件的首页显示word图标,表示该PPT已包含配套word讲稿。双击word图标可打开word文档。
- 特殊限制:
部分文档作品中含有的国旗、国徽等图片,仅作为作品整体效果示例展示,禁止商用。设计者仅对作品中独创性部分享有著作权。
- 关 键 词:
- Arcam DV88 dvd sm 维修 电路 原理图
 收音机爱好者资料库所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
收音机爱好者资料库所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。


 Marshall-9100-62-02-Schematic电路原理图.pdf
Marshall-9100-62-02-Schematic电路原理图.pdf